1. Which of the following variables cannot be expressed in quantitative terms?
(A) Socio-economic Status
(B) Marital Status
(C) Numerical Aptitude
(D) Professional Attitude
2. A doctor studies the relative effectiveness of two drugs of dengue fever. His research would be classified as
(A) Descriptive Survey
(B) Experimental Research
(C) Case Study
(D) Ethnography
3. The term ‘phenomenology’ is associated with the process of
(A) Qualitative Research
(B) Analysis of Variance
(C) Correlational Study
(D) Probability Sampling
4. The ‘Sociogram’ technique is used to study
(A) Vocational Interest
(B) Professional Competence
(C) Human Relations
(D) Achievement Motivation
Read the following passage carefully and answer questions from 5 to 10:
It should be remembered that the nationalist movement in India, like all nationalist movements, was essentially a bourgeois movement. It represented the natural historical stage of development, and to consider it or to criticize it as a working-class movement is wrong. Gandhi represented that movement and the Indian masses in relation to that movement to a supreme degree, and he became the voice of Indian people to that extent. The main contribution of Gandhi to India and the Indian masses has been through the powerful movements which he launched through the National Congress. Through nation-wide action he sought to mould the millions, and largely succeeded in doing so, and changing them from a demoralized, timid and hopeless mass, bullied and crushed by every dominant interest, and incapable of resistance, into a people with self-respect and self-reliance, resisting tyranny, and capable of united action and sacrifice for a larger cause.
Gandhi made people think of political and economic issues and every village and every bazaar hummed with argument and debate on the new ideas and hopes that filled the people. That was an amazing psychological change. The time was ripe for it, of course, and circumstances and world conditions worked for this change. But a great leader is necessary to take advantage of circumstances and conditions. Gandhi was that leader, and he released many of the bonds that imprisoned and disabled our minds, and none of us who experienced it can ever forget that great feeling of release and exhilaration that came over the Indian people.
Gandhi has played a revolutionary role in India of the greatest importance because he knew how to make the most of the objective conditions and could reach the heart of the masses, while groups with a more advanced ideology functioned largely in the air because they did not fit in with those conditions and could therefore not evoke any substantial response from the masses.It is perfectly true that Gandhi, functioning in the nationalist plane, does not think in terms of the conflict of classes, and tries to compose their differences. But the action he has indulged and taught the people has inevitably raised mass consciousness tremendously and made social issues vital. Gandhi and the Congress must be judged by the policies they pursue and the action they indulge in. But behind this, personality counts and colours those policies and activities. In the case of very exceptional person like Gandhi the question of personality becomes especially important in order to understand and appraise him. To us he has represented the spirit and honour of India, the yearning of her sorrowing millions to be rid of their innumerable burdens, and an insult to him by the British Government or others has been an insult to India and her people.
5. Which one of the following is true of the given passage?
(A) The passage is a critique of Gandhi’s role in Indian movement for independence.
(B) The passage hails the role of Gandhi in India’s freedom movement.
(C) The author is neutral on Gandhi’s role in India’s freedom movement.
(D) It is an account of Indian National Congress’s support to the working-class movement.
6. The change that the Gandhian movement brought among the Indian masses was
(A) Physical
(B) Cultural
(C) Technological
(D) Psychological
7. To consider the nationalist movement or to criticise it as a working-class movement was wrong because it was a
(A) historical movement
(B) voice of the Indian people
(C) bourgeois movement
(D) movement represented by Gandhi
8. Gandhi played a revolutionary role in India because he could
(A) preach morality
(B) reach the heart of Indians
(C) see the conflict of classes
(D) lead the Indian National Congress
9. Groups with advanced ideology functioned in the air as they did not fit in with
(A) objective conditions of masses
(B) the Gandhian ideology
(C) the class consciousness of the people
(D) the differences among masses
10. The author concludes the passage by
(A) criticising the Indian masses
(B) the Gandhian movement
(C) pointing out the importance of the personality of Gandhi
(D) identifying the sorrows of millions of Indians
11. Media that exist in an interconnected series of communication – points are referred to as
(A) Networked media
(B) Connective media
(C) Nodal media
(D) Multimedia
12. The information function of mass communication is described as
(A) diffusion
(B) publicity
(C) surveillance
(D) diversion
13. An example of asynchronous medium is
(A) Radio
(B) Television
(C) Film
(D) Newspaper
14. In communication, connotative words are
(A) explicit
(B) abstract
(C) simple
(D) cultural
15. A message beneath a message is labelled as
(A) embedded text
(B) internal text
(C) inter-text
(D) sub-text
16. In analog mass communication, stories are
(A) static
(B) dynamic
(C) interactive
(D) exploratory
17. Determine the relationship between the pair of words ALWAYS : NEVER and then select from the following pair of words which have a similar relationship :
(A) often : rarely
(B) frequently : occasionally
(C) constantly : frequently
(D) intermittently : casually
18. Find the wrong number in the sequence: 52, 51, 48, 43, 34, 27, 16
(A) 27
(B) 34
(C) 43
(D) 48
19. In a certain code, PAN is written as 31 and PAR as 35, then PAT is written in the same code as
(A) 30
(B) 37
(C) 39
(D) 41
20. The letters in the first set have certain relationship. On the basis of this relationship, make the right choice for the second set: AF : IK : : LQ : ?
(A) MO
(B) NP
(C) OR
(D) TV
21. If 5472 = 9, 6342 = 6, 7584 = 6, what is 9236?
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
22. In an examination, 35% of the total students failed in Hindi, 45% failed in English and 20% in both. The percentage of those who passed in both subjects is
(A) 10
(B) 20
(C) 30
(D) 40
23. Two statements I and II given below are followed by two conclusions (a) and (b). Supposing the statements are true, which of the following conclusions can logically follow ? Statements:
I. Some flowers are red.
II. Some flowers are blue.
Conclusions:
(a) Some flowers are neither red nor blue.
(b) Some flowers are both red and blue.
(A) Only (a) follows.
(B) Only (b) follows.
(C) Both (a) and (b) follow.
(D) Neither (a) nor (b) follows.
24. If the statement ‘all students are intelligent’ is true, which of the following statements are false?
(i) No students are intelligent, (ii) Some students are intelligent, (iii) Some students are not intelligent.
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (i) and (iii)
(C) (ii) and (iii)
(D) (i) only
25. A reasoning where we start with certain particular statements and conclude with a universal statement is called
(A) Deductive Reasoning
(B) Inductive Reasoning
(C) Abnormal Reasoning
(D) Transcendental Reasoning
26. What is the smallest number of ducks that could swim in this formation – two ducks in front of a duck, two ducks behind a duck and a duck between two ducks?
(A) 5
(B) 7
(C) 4
(D) 3
27. Mr. A, Miss B, Mr. C and Miss D are sitting around a table and discussing their trades.
(i) Mr. A sits opposite to the cook.
(ii) Miss B sits right to the barber
(iii) The washerman sits right to the barber
(iv) Miss D sits opposite to Mr. C
What are the trades of A and B?
(A) Tailor and barber
(B) Barber and cook
(C) Tailor and cook
(D) Tailor and washerman
28. Which one of the following methods serve to measure correlation between two variables?
(A) Scatter Diagram
(B) Frequency Distribution
(C) Two-way table
(D) Coefficient of Rank Correlation
29. Which one of the following is not an Internet Service Provider (ISP)?
(A) MTNL
(B) BSNL
(C) ERNET India
(D) Infotech India Ltd.
30. The hexadecimal number system consists of the symbols
(A) 0 – 7
(B) 0 – 9 , A – F
(C) 0 – 7, A – F
(D) None of these
31. The binary equivalent of (–15)10 is (2’s complement system is used)
(A) 11110001
(B) 11110000
(C) 10001111
(D) None of these
32. 1 GB is equal to
(A) 230 bits
(B) 230 bytes
(C) 220 bits
(D) 220 bytes
33. The set of computer programs that manage the hardware/software of a computer is called
(A) Compiler system
(B) Operation system
(C) Operating system
(D) None of these
34. S/MIME in Internet technology stands for
(A) Secure Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension
(B) Secure Multimedia Internet Mail Extension
(C) Simple Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension
(D) Simple Multimedia Internet Mail Extension
35. Which of the following is not covered in 8 missions under the Climate Action Plan of Government of India?
(A) Solar power
(B) Waste to energy conversion
(C) Afforestation
(D) Nuclear energy
36. The concentration of Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) in drinking water should not exceed
(A) 500 mg/L
(B) 400 mg/L
(C) 300 mg/L
(D) 200 mg/L
37. ‘Chipko’ movement was first started by
(A) Arundhati Roy
(B) Medha Patkar
(C) Ila Bhatt
(D) Sunderlal Bahuguna
38. The constituents of photochemical smog responsible for eye irritation are
(A) SO2 and O3
(B) SO2 and NO2
(C) HCHO and PAN
(D) SO2 and SPM
39. Assertion (A): Some carbonaceous aerosols may be carcinogenic.
Reason (R): They may contain polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs).
(A) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is correct, but (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false, but (R) is correct.
40. Volcanic eruptions affect
(A) atmosphere and hydrosphere
(B) hydrosphere and biosphere
(C) lithosphere, biosphere and atmosphere
(D) lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere
41. India’s first Defence University is in the State of
(A) Haryana
(B) Andhra Pradesh
(C) Uttar Pradesh
(D) Punjab
42. Most of the Universities in India
(A) conduct teaching and research only
(B) affiliate colleges and conduct examinations
(C) conduct teaching/research and examinations
(D) promote research only
43. Which one of the following is not a Constitutional Body?
(A) Election Commission
(B) Finance Commission
(C) Union Public Service Commission
(D) Planning Commission
44. Which one of the following statements is not correct?
(A) Indian Parliament is supreme.
(B) The Supreme Court of India has the power of judicial review.
(C) There is a division of powers between the Centre and the States.
(D) There is a Council of Ministers to aid and advise the President.
45. Which one of the following statements reflects the republic character of Indian democracy?
(A) Written Constitution
(B) No State religion
(C) Devolution of power to local Government institutions
(D) Elected President and directly or indirectly elected Parliament
46. Who among the following appointed by the Governor can be removed by only the President of India?
(A) Chief Minister of a State
(B) A member of the State Public Service Commission
(C) Advocate-General
(D) Vice-Chancellor of a State University
47. If two small circles represent the class of the ‘men’ and the class of the ‘plants’ and the big circle represents ‘mortality’, which one of the following figures represent the proposition ‘All men are mortal.’ ?
Answer: C
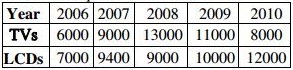
The following table presents the production of electronic items (TVs and LCDs) in a factory during the period from 2006 to 2010. Study the table carefully and answer the questions from 48 to 52:
48. In which year, the total production of electronic items is maximum?
(A) 2006
(B) 2007
(C) 2008
(D) 2010
49. What is the difference between averages of production of LCDs and TVs from 2006 to 2008?
(A) 3000
(B) 2867
(C) 3015
(D) 2400
50. What is the year in which production of TVs is half the production of LCDs in the year 2010?
(A) 2007
(B) 2006
(C) 2009
(D) 2008
51. What is the ratio of production of LCDs in the years 2008 and 2010?
(A) 4 : 3
(B) 3 : 4
(C) 1 : 3
(D) 2 : 3
52. What is the ratio of production of TVs in the years 2006 and 2007?
(A) 6 : 7
(B) 7 : 6
(C) 2 : 3
(D) 3 : 2
53. Some students in a class exhibit great curiosity for learning. It may be because such children
(A) Are gifted
(B) Come from rich families
(C) Show artificial behaviour
(D) Create indiscipline in the class
54. The most important quality of a good teacher is
(A) Sound knowledge of subject matter
(B) Good communication skills
(C) Concern for students’ welfare
(D) Effective leadership qualities
55. Which one of the following is appropriate in respect of teacher student relationship?
(A) Very informal and intimate
(B) Limited to classroom only
(C) Cordial and respectful
(D) Indifferent
56. The academic performance of students can be improved if parents are encouraged to
(A) supervise the work of their wards
(B) arrange for extra tuition
(C) remain unconcerned about it
(D) interact with teachers frequently
57. In a lively classroom situation, there is likely to be
(A) occasional roars of laughter
(B) complete silence
(C) frequent teacher-student dialogue
(D) loud discussion among students
58. If a parent approaches the teacher to do some favour to his/her ward in the examination, the teacher should
(A) try to help him
(B) ask him not to talk in those terms
(C) refuse politely and firmly
(D) ask him rudely to go away
59. Which of the following phrases is not relevant to describe the meaning of research as a process?
(A) Systematic Activity
(B) Objective Observation
(C) Trial and Error
(D) Problem Solving
60. Which of the following is not an example of a continuous variable?
(A) Family size
(B) Intelligence
(C) Height
(D) Attitude





No comments:
Post a Comment